Photo and roses laid at St. Petersburg gravestie of Yevgeny Prigozhin during his funeral on August 29, 2023. On August 23, 2023, the owner of ChVK Vagnera, popularly known in the Russian Federation as Gruppa Vagnera (the Wagner Group), Yevgeny Prigozhin and nine other passengers were killed in a jet crash north of Moscow. The crash came only two months after the Wagner Group Rebellion in the Russian Federation. For those unfamiliar with that episode, on June 23, 2023, Prigozhin drove elements of his military organization into the Russian Federation from Ukraine with the purpose of removing by force the Russian Federation Defense Minister Russian Army General Sergei Shoigu and ostensibly Chief of the General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation), Russian Army General Valery Gerasimov, from their posts. A deal brokered by Belarus President Alexander Lukashenko was struck that caused the Wagner Group to halt. The Wagner Group, a private military corporation, had fought alongside the Russian Federation Armed Forces. Since the first day of its special military operation in Ukraine. Prigozhin, became greatly frustrated over the delinquencies, deficiencies, and ineptitude of the Russian Federation military leadership which his organization has been directed to work under. If not the evidence itself, the manner in which the air disaster transpired, and a history of reported behavior by Russian Federation President Vladimir Putin, led many see logic behind the common wisdom that he was involved. Yet, it was certainly not enough to prove he ordered albeit a not-so-unique form of execution. As of the time of this writing, many major events have occurred since the Prigozhin’s jet crash. Yet, there seems something more unique about the Prigozhin jet crash story. There remains be much to understand regarding Prigozhin’s denouement and the closing of another tragic chapter of Putin’s life. Examining the facts of this episode, greatcharlie has sought to provide a better picture in particular of the interplay of light and dark forces that guide Putin’s behavior.
On August 23, 2023, a private Embraer jet flying to St. Petersburg crashed north of Moscow killing all ten passengers onboard. Onboard was the owner of ChVK Vagnera, popularly known as Gruppa Vagnera (the Wagner Group), Yevgeny Prigozhin, two other top Wagner Group officials, to include Dmitry Utkin, Prigozhin’s four bodyguards and a crew of three. The crash garnered international attention as it came only two months after the Wagner Group Rebellion in the Russian Federation. For those unfamiliar with that episode, on June 23, 2023, Prigozhin drove elements of his military organization into the Russian Federation from Ukraine with the purpose of removing by force the Ministr Oborony Rossijskoj Federacii (Minister of Defense of the Russian Federation hereinafter referred to as the Russian Federation Defense Minister) Russian Army General Sergei Shoigu and ostensibly Chief of General’nyy shtab Vooruzhonnykh sil Rossiyskoy Federatsii (General Staff of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation), Russian Army General Valery Gerasimov, from their posts. Prigozhin’s Wagner Group troops advanced to just 120 miles (200 kilometers) from Moscow. However, a deal brokered by Belarus President Alexander Lukashenko was struck that caused the Wagner Group to halt. Prigozhin withdrew his forces to avoid what all sides feared would be the further “shedding Russian blood.” The Wagner Group, a private military corporation, had fought alongside the Russian Federation Armed Forces since the first day of its special military operation in Ukraine. Prigozhin, became greatly frustrated over the delinquencies, deficiencies, and ineptitude of the Russian Federation military leadership which his organization has been directed to work under. By 2023, Prigozhin unquestionably behaved as if he were frenzied, and perhaps justifiably and reasonably so, with the great injustice put upon Wagner Group troops in Ukraine as well as the troops of the Russian Federation Armed Forces during the Spetsial’noy Voyennoy Operatsii (Special Military Operation). On June 23, 2023, however, Prigohzin shifted from simply accusing Shoigu and Gerasimov of poorly conducting by then a 16-month-long special military operation when events took a graver turn. Prigozhin accused forces under the direction of Shoigu and Gerasimov of attacking Wagner Group camps in Ukraine with rockets, helicopter gunships and artillery and as he stated killing “a huge number of our comrades.” The Russian Federation Defense Ministry denied attacking the camps. Prigozhin then set off with elements of the Wagner Group to attack the Defense Minister in Moscow.
Assuredly, if Prigozhin’s deadly jet crash was not accidental and ordered by the highest authorities in the Russian Federation government, the decision was most likely multifactorial. Many opinions have offered by analysts and experts on the Russian Federation on how Russian Federation President Vladimir Putin benefitted from the action were also offered. If not the evidence itself, the manner in which the air disaster transpired, and a history of reported behavior by Russian Federation President Vladimir Putin, led many see logic behind the common wisdom that he was involved. Yet, it is certainly not enough to prove he ordered such a not-so-unique form of execution in authoririan regimes, also occasionally witnessed in democracies. Omnia mors poscit. Lex est, non pœna, perire. (Death claims all things. It is law, not punishment, to die.)
The media cycle on the untimely death of Prigozhin and senior commanders of his Wagner Group appeared to reach it apogee by the start of September 2023. However, Putin seemingly sought to pry the door to it open. For reasons that are not completely clear, and a timing not easily understood by greatcharlie, on October 5, 2023, Putin suggested that the investigation of Russian Federation’s investigative Committee was not barren, and its head reported to him that evidence was found indicating that the jet crash which killed Prigozhin was caused by hand grenades detonating inside the aircraft, not by a missile attack. Although frugal with information immediately following the air disaster and days that followed, the extraordinary and surprising revelations by Putin of additional information garnered during the investigation was provided in a very public setting. Similarly surprising was the fact that Putin also went as far as to make disparaging suggestions about the use of narcotics among passengers on his jet, ignoring Prigozhin’s family’s pain and disregarding the couteousy of displaying respect for the dead. For those interested observers interested in Prigozhin’s demise, the way in which it occurred provided a proper mystery.
As of the time of this writing, many major events have occurred since the Prigozhin’s jet crash. The 2023 North Korea–Russia summit between Putin and Democratic People’s Republic of Korea Chairman Kim Jung-un was held in Moscow on September 23, 2023. Putin in his first foreign visit after the International Criminal Court in The Hague issued a warrant for his arrest visited Kyrgyzstan on October 12, 2023. Putin then visited People’s Republic of China President Xi Jinping in Bejing on October 17, 2023. Each event provided ample opportunity to further assess Putin’s words and behavior to construct a firmer understanding of the man and his decisionmaking. Yet, there seems something more unique about the Prigozhin jet crash story. After all, Putin and Prigozhin, at least for a time, were true friends. That was somewhat evident in Putin’s initial public comments on the crash. In many respects, for Putin, the deadly episode amounted to a private tragedy within what seemed a public conflict. Many details will likely remain kept from both the public and the newsmedia. Still, from what has been been presented to the public, there remains be much to gain regarding Prigozhin’s denouement and the closing of another tragic chapter of Putin’s presidency. Examining the facts of this episode, greatcharlie has sought to provide a better picture in particular of the interplay of light and dark forces that guide Putin’s behavior.
Unless there is additional information so newsworthy concerning Prigozhin that it cannot be dismised or avoided, greatcharlie believes this will be it last entry on the passed-on Wagner Group owner. Still, as has been the case with its previous posts, greatcharlie hopes this essay will stimulate among readers, particularly students, new lines of thought, even kernels of ideas on how US foreign and national security policy analysts and decisionmakers, as well as analysts and decisionmakers of other governments might proceed concerning the Russian Federation. Certainly, it would be humbled to see it take its place among ideas being exchanged internationally on Ukraine and Putin through which it may eventually become part of the greater policy debate. Though, for greatcharlie, it would be satisfying enough to have this commentary simply stand alone as one of its many posts on foreign and national security policy. Stat sua cuique dies; breve et irreparabile tempus omnibus est vitæ; sed famam extendere factis, hoc virtutis opus. (Each one has his appointed day; short and irreparable is the brief life of all; but to extend our fame by our deeds, this is the work of virtue.)
Police guard site of crash of Yevgeny Prigozhin’s private jey in the Tver region of the Russia, Feration, August 24, 2023 (above). The media cycle on the untimely death of Prigozhin and senior commanders of his Wagner Group appeared to reach it apogee by the start of September 2023. However, Putin seemingly sought to pry the door to it open. For reasons that are not completely clear, and a timing not easily understood by greatcharlie, on October 5, 2023, Russian Federation President Vladimir Putin suggested that the investigation of Russian Federation’s investigative Committee was not barren, and its head reported to him that evidence was found indicating that the jet crash which killed Prigozhin was caused by hand grenades detonating inside the aircraft, not by a missile attack. Although frugal with information immediately following the air disaster and days that followed, the extraordinary and surprising revelations by Putin of additional information garnered during the investigation was provided in a very public setting. Similarly surprising was the fact that Putin also went as far as to make disparaging suggestions about the use of narcotics among passengers on his jet, ignoring Prigozhin’s family’s pain and disregarding the couteousy of displaying respect for the dead. For those interested observers interested in Prigozhin’s demise, the way in which it occurred provided a proper mystery.
The Grenade Gambit
(Beware the man who offers answers when no questions are asked, excuses when their is no apparent misstep or error, an alibi when there is no allegation, or a most apparent contrived defense when there is no accusation, as such virtual confessions often indicate the individual is so tormented by the possible discovery of their own errant or surreptitious behavior to the extent they can only see the world from their own anxiously insecure or unrepentantly deceitful mindset, and perhaps seeks to manipulate what they imagine others likely think.) As aforementioned, on October 5, 2023, meeting of the Valdai Discussion Club in the Black Sea resort of Sochi. Putin suggested the jet was blown up from inside, basing his comments on a report he received from the head of Russia’s investigative committee a few days before. Putin stated: “Fragments of hand grenades were found in the bodies of those killed in the crash.” He continued: “There was no external impact on the plane–this is already an established fact.” Putin cut short his comments concerning a grenade or grenades that may have been detonated on board. Yet, in support of the idea of any mishandling of ordinance onboard, Putin stated that he thought investigators remiss in failing to perform alcohol and drug tests on the bodies of those who died in the jet crash. Regarding his reason for that concern, Putin noted that in the past, quantities of cocaine had been found in the Wagner Group’s headquarters in St. Petersburg. With regard to Putin’s comments on any external impact, he was apparently rebuffing assertions made by anonymous US sources just after the jet crash suggesting it had been shot down. Russian Federation officials investigating the jet crash have not reported publicly on the cause as of this writing. Ad calamitatem quilibet rumor valet. (Any rumor is sufficient against calamity (i.e., when a disaster happens, every report confirming it obtains ready credence)
With little else to go on, it is assessed by greatcharlie that concerning the grenade fragments being found, Putin may have actually been presenting the truth. In the abstract, surely, such an explanation is not too far from possible. (Surely “evidence” now exists to fully support the Russian Federation President’s statements. It is hard to imagine who would be so daring in the Russian Federation to challenge Putin’s word on what may have transpired.) What remains unclear is why Putin would publicly express such derogatory information on one who was a prominent member of his retinue for some time. Those willing give Putin the benefit of the doubt might accept his negatuve comments as an odd, yet understandable and natural expression of his anxiety. To that extent, the public exposition may have assisted Putin in exercising the ghosts. Maybe they would proffer that it was an effort by Putin to persuade himself that there was some logic in the senseless, troubling circumstance of Prigozhin’s loss. Anger is a stage of grieving. Born Jacques Anatole François Thibault, known as Anatole France (April 16, 1844-October 12, 1924) was a French poet, journalist, and novelist. Considered in his day as the ideal French man of letters. he won the 1921 Nobel Prize in Literature in recognition of his literary achievements. In Part II, chapter 4, of The Crime of Sylvestre Bonnard (1881), Thibault wrote: Tous les changements, même les plus so ont leur mélancolie, car ce que nous quittons, c’est une partie de nous-mêmes; il faut mourir à une vie pour entrer dans une autre. (All changes, even the most longed for, have their melancholy; for what we leave behind us is a part of ourselves; we must die to one life before we can enter another.)
Under another line of thought, it might be considered that because he is always politically minded, and posturing to present the best picture of himself possible, Putin’s remarks were most likely–doubtlessly–curated, calculated, but mainly so as part of an effort to convince the Russian people that he could not have committed such as heinous act. Indeed, conceivably Putin offered the new facts with the hope of better shaping the Russian people’s conclusions on the incident and opinion of his government. He seems on a quest to create a more favorable image of himself on the matter given so much bad has resulted from his Ukraine enterprise. It is surely an uphill battle. After all, few in the world seemed to doubt that he ordered or members of his regime were complicit in responsible for the crash of Prigozhin’s jet.
Interestingly enough, if Putin initially believed what he offered in Sochi was logical, he went a long way to make connections that were hardly certain. It would require perhaps too much imagination think senior commanders of the Wagner Group, having traveled together for years without incident, were doing any more than discussing important matters in camera onboard the jet as they made their way in the direction of St. Petersburg. It would require too little imagination to believe Prigozhin’s private jet was nothingless than le bateau iver–the boat of drunks–aboard which passengers werante perhaps in an inebriated state playing “hot potato” with a live grenade and soething went terribly wrong or tempers flared during a heated argument and disregulated party to the exchange well-beyond making a deadly threat, pulled the pin on a grenade. Even that would seem possible if Putin believes the imagination of the Russian people is boundless. Evidently, the passengers had traveled on more than one occasion on similar jets, perhaps the self-same one, without any fatal incidents with ordinance. In any event, Putin apparently does not want to leave the matter for the Russian people to reach their own conclusions on what is true or not.
If in some moment of intense quiet reflection, Putin should conjer any additional insights on the Prigozhin case, one would imagine that he might be less likely to share it publicly it as the story now thoroughly belongs to the past. Quand on ne peut revenir en arrière, on ne doit se préoccuper que de la meilleure façon d’aller de l’avant.
Common Wisdom in the West: The Prigozhin Jet Crash Was a “Mafia Style” Act by Putin
Comparisons with what some in the mainstream Western newsmedia have alleged as Putin’s Mafia act and his behavior as a Mafia Don as often depicted in novels and Hollywood films of the organized crime genre, are too much for greatcharlie to contenance. It acknowledges that it was all most inappropriate given that ten individuals died in a jet crash and not a fictional event. Such thinking is perfectly understandable as nearly everything discussed for mass public consumption is reduced to banal amusement. While this popular explanation of Mafia tactics, technique, procedures, and methods in drawn from the abstract, in most cases, such expertise, expressed with confidence, is drawn from novels and Hollywood films, “The Godfather”, “Goodfellas”, and “The Sopranos.” Then again, perchance some commentators are signalling a desire to reveal even greater information made known to them through unnerving contacts with organized crime groups, but that would be unlikely. Knowing how deadly such organize crime figures can be, they would hardly seek on such a point to reveal confidences of ghastly acts shared with those sadistic individuals.
As of the time of this writing, early October 2023, the return to secondary school–rentrée–is complete. At that level, nothing less could expectedly be heard at the cafeteria tables as students who might have a passing interest in world affairs. Any similar theories of this kind offered by serious analysts, journalists, and newsmedia commentators, could at best be recognized as faulty humor, pretension, or some unfortunate internal response to the cognitive collective imperative rather than investigated facts. Such surmisal could certainly not be viewed as an informed opinion. It is stated again that there are no publicly reported facts that indicate there was an effort to disable or down Prigozhin’s jet. Even if such existed, there is nothing that would point to Putin as being behind the air tragedy directly or indirectly. There is no proof of orders being issued from Putin or others in the Kremlin. There certainly has been no mea culpa from covert operatives from the Russian Federation Defense Ministry, the security services, or “contractors”. Furthermore, no offical information released publicly indicates ordinance was detonated onboard the jet.
Putin and Prigozhin as Associates
Wilhelm Richard Wagner (May 23, 1813 to February 13, 1883) was a German composer, conductor, and ptolemicist, known mainly for his operas. He is categorized as part of the 19th century musical movement of nationalism. In his compositions, Wagner would synthesize elements of disciplines such as music, poetry, architecture, painting, and others. Wagner described his inclusive vision in a series of essays published between 1849 and 1852 as the concept of Gesamtkunstwerk, or “total work of art.” Over the years his concept has influenced work in diverse fields to include in some part, intelligence analysis where accepted, in support of the examination of individuals, events, and policy decisionmaking beyond the surface. To that extent, in making use of what it feels is an apropos use–at least a pinch–of the artistic genre of film to conceptualize, greatcharlie takes into consideration the profound remarks of Austrian film director Marie Kreutzer. (It must be noted that no connection at all is implied between the talented and inspiring Kreutzer and Wagner.) As a result researching through history for her films, Kreutzer has stated often, “Every biography is an interpretation of the facts.” Developing a credible character, in the relative in the abstract, she suggests it is paramount to stay true to the personality one reads about than presenting just the facts, not simply ticking historical boxes. Using those available facts and guided by its understanding of the personalities of both Putin and Prigozhin, greatcharlie offers a new analysis, a well-grounded interpretation of their relationship to create pertinent, credible and useful insights,
The relationship between Putin and Prigozhin began with friendship and cordially, and not at least solely or primarily, a mutual effort to seek respective gain. The two men appreciated each other. During the initial years of his pesidency, Prigozhin was observed often in Putin orbit, but he certainly was not a typical member of his retinue. Prigozhin was neither siloviki, formerly employed in the Komitet Gosudarstvennoy Bezopasnosti (the Committee for State Security) or KGB, nor Chekisty, having a father or grandfather who worked in the Soviet Union’s Narodnyi Komissariat Vnutrennikh Del (People’s Commissariat of Internal Affairs) or NKVD–an earlier iteration of the security services, famed during World War II and the start of the Cold War–as Putin is. (Surely, not everyone close to Putin today possess such attributes. As time goes on, that will doubtlessly become more the case.) Quite the opposite of possessing security service background, in the 1980s and bit of the 1990s when any of that might have been possible. In November 1979, 18-year-old Prigozhin was caught stealing and given a suspended sentence. However, later in 1981, he and several accomplices, according to Meduza, were arrested for robbing apartments in upscale neighborhoods. He would be convicted on four charges to include robbery, fraud, and involving teenagers in prostitution. Prigozhin violated the terms of his confinement “on a regular basis” until 1985, when in solitary confinement, he started to “read intensely.” In 1988, the Russian Supreme Court reduced his sentence to 10 years, noting that he had “began corrective behavior.” In order to earn money, he requested to be transferred to a residential colony for timber work, which the document characterizes as “extremely hard labor.” After serving 9 years of his 13 year sentence, Prigozhin was freed in 1990. Immediately after his release, Prigozhin briefly returned to skiing, by working as a ski trainer at an athletics school in Leningrad. In 1990, Prigozhin studied at the Leningrad Chemical and Pharmaceutical Institute–now the Saint Petersburg State Chemical Pharmaceutical Academy–but was expelled.
However, from that point, Prigozhin by fate, received the firm support of his family, joining its street food vending business. Having knack for the work he successfully expanded the business and gained some notoriety. From street vending, Prigozhin entered the established food service industry. Next, Prigozhin entered the gambling business. In that realm, he linked up with a school chum, Boris Spektor along with another hard charging entrepreneur, Igor Gorbenko, brought Prigozhin on as CEO of Spektr (Spectrum) CJSC which established the first casinos in St. Petersburg. The trio would jointly start many other enterprises in diverse industries in the 1990s, including construction, marketing research, and import-export.
Through his joint ownership of the gambling businesses, it has been suggested by the Russian Federation independent news source, Novaya Gazeta, that Prigozhin may have first encountered Putin or at least began interacting with him on a professional level. Putin at the time had been chairman of the supervisory board for casinos and gambling since 1991. What started as a business acquaintance became a good acquaintance. Putin was reportedly intrigued by what could be characterized as Prigozhin’s rags-to-riches story. In 1997, Prigozhin and a business partner, founded a second restaurant, New Island, a floating eatery that became one of the most fashionable dining spots in the city. The New Island Restaurant also became a favorite of Putin, who by then was the former deputy mayor of the city. In Part 7, of his biography/memoir First Person: An Astonishingly Frank Self-Portrait by Russia’s President (Public Affairs, 2000), Putin explains that once his superior and political mentor, the Mayor of Leningrad Alexander Sobchak, lost his re-elect bid, he faced a lean and trying period as the erstwhile deputy mayor of the city. He was unemployed for a few months and sufficient money was not coming into the household. His mother was also in the picture. Putin was greatly concerned for his future. He was making calls, wearing out shoe leather, and knocking on all doors with the hope of securing something appropriate. As the story goes, Putin’s luck changed immensely. Putin would still visit Prigozhin’s popular St. Petersburg restaurant. That allowed Putin to keep in the mix of things, hobnobbing with elites. The gregarious Prigozhin most likely would have insisted that Putin dine “on the house”. Prigozhin was very likely a friend indeed at a time of need for Putin. If what has been surmised here truly was the case, it would do much to explain in good part why Putin was considerably generous toward Prigozhin in later years. (In its March 31, 2017 post entitled, “Book Review: Vladimir Putin, First Person: An Astonishingly Frank Self-Portrait by Russia’s President (Public Affairs, 2000)”, greatcharlie provides a review of Putin’s memoir/biography.)
Putin’s generosity toward Prigozhin began in full-bore in 2000 when the newly minted Russian Federation President brought the then-Prime Minister of Japan, Yoshiro Mori, to a professional dinner at New Island out of sheer interest. The following year, Putin brought Jacques Chirac, then former President of France, to Prigozhin’s “buoyant” restaurant. He brought US President George W. Bush to the New Island in 2002. Prigozhin personally served food to Putin’s foreign guests. Imaginably, all of his guests left the New Island with appetites “keener” for Russian cuisine afterwards. Putin hosted his own birthday party at the New Island in 2003.
In those initial halcion years of their burgeoning friendship, Prigozhin been able to make use of his own unique sensibilities to understand Putin’s thinking and feelings. Beyond just liking Prigozhin, Putin displayed his feelings for his friend before everyone. The Russian Federation independent newsmedia source Meduza reported Putin welcomed Prigozhin as “one of the boys.” The five-act grand opera composed originally in French by Giuseppe Verdi “Don Carlos” is based on the dramatic play Don Karlos, Infant von Spanien (Don Carlos, Infante of Spain) by Friedrich Schiller. Verdi additionally borrowed portions of Eugène Cormon’s 1846 play Philippe II, Roi d’Espagne. In Act I, Carlos’ dear friend Rodrigue, Marquis of Posa, who has just arrived from the oppressed land of Flanders, enters. The two greet each other joyfully with the aria: “J’étais en Flandres”. Posa asks for Carlos’ aid on behalf of the suffering people there. Carlos reveals that he loves his stepmother. Posa is first shocked, but then sympathetic. He encourages Carlos to leave Spain and go to Flanders, and to forget his pain by focusing on political activity there. The two men through a tenor/baritone duet swear eternal friendship in French titled, “Dieu, tu semas dans nos âmes”, and in Italian titled, “Dio, che nell’alma infondere”. The lyrics of the duet in Italian are: “Dieu, qui de nos coeurs sincères / As fait les coeurs de deux frères, / Accepte notre serment! / Nous mourrons en nous aimant! / Ah! Dieu, tu semas dans nos âmes, etc” (“God, who of our sincere hearts / has made the hearts of two brothers, / receive our vow! / We will die loving each other! / Ah! God, you scattered in our souls, etc.”)
A reasonable assessment by experts or an informed guess by any keen observer before the special military operation began in 2022 would have been that Prigozhin would unlikely be separated from Putin anytime too soon. Having observed Prigozhin closely during their earliest interactions, Putin obviously concluded that he could well-serve his needs. By 2003, he left his business partners and established his own independent restaurants. One of Prigozhin’s companies, Concord Management and Consulting, founded in 1996, was awarded numerous government contracts. They were opportunities of a lifetime. Bien mal acquis ne profite jamais.
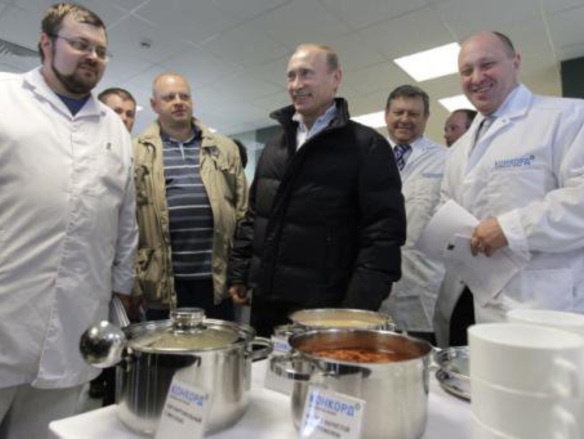
Putin (center) visits Prigozhin (right) at a Concord Management and Consulting facility in 2010. In the initial halcion period of their burgeoning friendship in the early 2000s, Prigozhin been able to make use of his own unique sensibilities to understand Putin’s thinking and feelings. Beyond just liking Prigozhin, Putin displayed his feelings for his friend before everyone. The Russian Federation newsmedia source Meduza reported Putin welcomed Prigozhin as “one of the boys.” A reasonable assessment by experts or an informed guess by any keen observer before the special military operation began in 2022 would have been that Prigozhin would unlikely be separated from Putin anytime too soon. Having observed Prigozhin closely during their earliest interactions, Putin obviously concluded that he could well-serve his needs. By 2003, he left his business partners and established his own independent restaurants. One of Prigozhin’s companies, Concord Management and Consulting, founded in 1996, was awarded numerous government contracts. They were opportunities of a lifetime.
In 2007, under the National Education Project, the Russian Federation government sought to improve catering in educational institutions in fourteen of the country’s regions. They introduced a program titled “innovative on-board lunches” for Russian schoolchildren. Сonсord received multiple contracts under that program. Following that, Prigozhin signed several federal government contracts totaling at least $3.1 billion. Prigozhin was linked to the oil industry as well. His companies reportedly received a percentage of Syria’s oil revenue in exchange for protecting its oil fields from the virulent Islamic terrorist organization, ISIS. A portion of the profits from his contracts with the Russian Federation Defense Ministry were alleged to have been used to start and fund the Internet Research Agency. It has been suggested that Prigozhin was advised by government sources to use his funds in this manner. The Internet Resource Agency, known also as Glavset, was a St. Petersburg-based technological company seeking to promote disinformation campaigns both domestically and abroad.
In 2014, Prigozhin invested a portion of his sizable wherewithal to develop a private military corporation, ChVK Vagnera–the Wagner Group. Although private military companies were not permitted under law in the Russian Federation at the time, the organization and others were endorsed in April 2012 by Putin, then Russian Federation Prime Minister, during an address to the State Duma. Headquartered in St. Petersburg, the Wagner Group engaged in actions externally in support of the Russian Federation’s overt and covert foreign and national security objectives. The Wagner Group is known to have deployed its units in the War in Donbas (2014–2022); Syrian Civil War, (2015–2016); the South Sudanese Civil War (2013-2020); the Central African Republic Civil War (2013-2014); the Second Libyan Civil War (2014-2020); the Sudanese Revolution (2018-2019); Venezuelan presidential crisis (2019-2023); and the Mali War (2012-present). Concerning the special military operation in Ukraine or any matter in which both men’s interests were concerned, Prigozhin never publicly expressed dissatisfaction with Putin nor has he ever stated anything he believed deep in his heart was derogatory about him. He hHd always spoken of him in endearing terms. When originally coordinating the Wagner Group’s with Russian Federation Armed Forces, according to the Guardian, Prigozhin would refer to Putin in those meetings as “Papa” which served to reflect his closeness to him as well as his fealty. It is unclear how the Guardian came by this picture of Prigozhin’s meetings within the Russian Federation Defense Ministry. Prigozhin would unlikely have wished to foment dissent against “Papa,” his dear leader. That would never have been Prigozhin’s intention, nor will it ever be. This is stated by greatcharlie with recent events most firmly in mind. Yet, as aforementioned, Prigozhin, became greatly frustrated over the delinquencies, deficiencies, and ineptitude of the Russian Federation military leadership which his organization has been directed to work under. By 2023, Prigozhin unquestionably behaved as if he were frenzied, and perhaps justifiably and reasonably so, with the great injustice put upon Wagner Group troops in Ukraine as well as the troops of the Russian Federation Armed Forces during the Spetsial’noy Voyennoy Operatsii (Special Military Operation). On June 23, 2023, however, Prigohzin shifted from simply accusing Shoigu and Gerasimov of poorly conducting by then a 16-month-long special military operation when events took a graver turn. Prigozhin accused forces under the direction of Shoigu and Gerasimov of attacking Wagner Group camps in Ukraine with rockets, helicopter gunships and artillery and as he stated killing “a huge number of our comrades.” The Russian Federation Defense Ministry denied attacking the camps. Prigozhin then set off with elements of the Wagner Group to attack the Defense Minister in Moscow.
Prigozhin should have been savvy enough to know that if he forced Putin to choose between Shoigu and himself, he would very well have lost. Putin showed considerable regard for Prigozhin but even greater regard for Shoigu both professionally and privately for a longer time. Putin at one time would make regular recreational visits to Shoigu’s place of birth, the mystical land of Tuva. He would often invite foreign guests to come along. Putin’s conversations with Shoigu have always been a bit different than those with others. Putin needs a close confidant with a firm grip on the reigns of all matters of or pertaining to defense. In fact, for him, it is a priority. Shoigu is responsible for the management not only of the Russian Federation’s conventional forces but also its all important strategic nuclear triad and all of its supporting military elements.
It might have been plausible enough for Prigozhin to do the heavy lifting politically in advance of committing his Wagner Group troops to ensure that he and his unit commanders would play a greater role in decisionmaking on how Wagner Group capabilities would be integrated into the future planning of cooperative operations with the Russian Federation Armed Forces in Ukraine. His démarche might have included insisting that the Wagner Group would always have a say on where they would be deployed on the ground, missions it would accept, and how they would perform them. Apparently nothing of the kind happened.
Omnia sunt hominum tenui pendentia filo; et subito casu, quæ valuere, ruunt. (All things human hang by a slender thread; and that which seemed to stand strong all of a sudden falls and sinks in ruins.) Competition for Putin’s attention surely comes in from all directions, and it is likely greater now than ever. He and his staff seem to be able to handle that. Prigohzin likely knew that Putin really did not need at any point during the flailing special military operation was an extra problem that from one angle might boil down to him, at least initially, as mere in-house bickering between two close associates. As noted in greatcharlie’s June 1, 2023 post entitled, “Commentary: Will the Ukraine War’s Course Stir Putin to Alter His Thinking and Seek Novel Ways Either to Win or to Reach a Peace Deal?”, Prigozhin was someone seemingly well-able to discern how much pressure is being brought to bear on Putin, and see great risk in overburdening him. For loyal subordinates such as Prigozhin, Putin was always the priority. What Putin thought was of the utmost importance to Prigozhin. There can be little doubt in greatcharlie’s mind that Prigozhin greatly concerned himself with the trying times Putin had been facing following his decision to intervene in Ukraine. Going out on a limb, greatcharlie states that it is very hard to believe that Prigozhin, regardless of any likely sense of obligation, would ever intentionally acted in a way to bring a shadow upon Putin’s life. That being stated, he was not always on target when it came to understanding Putin’s perspective. It appears that the more complex a situation was, the less effective Prigozhin’s “foresight” and “intuition” became. It seems something went terribly wrong around the time of the Wagner Group Rebellion.
Le bon critique est celui qui raconte les aventures de son âme au milieu des chefs-d’œuvre. Ernst Julius Günther Röhm (November 28, 1887-July 1, 1934) was a close friend and early ally of Adolf Hitler, A former military officer and senior member of the Röhm co-founded and led the Sturmabteilung (SA), thel paramilitary wing of the Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei (National Socialist German Workers’ Party or Nazi Party) , from 1931 to 1934. The SA played a key part in Hitler’s ascension. The are many intriguing parallels, mutatis mutandis, concerning the two relationships between the two national leader and two paramilitary heads, to the extent that much as Prigozhin fell out with Putin, Rõhm fell out with Hitler. In 1919, Röhm joined the Deutsche Arbeiterpartei (German Workers’ Party), the precursor of the Nazi Party formed in 1920, and became a close associate of Adolf Hitler. When he joined the German Workers Party, Röhm had already begun using his military ties to develop paramilitary groups across Germany in service of Hitler. Leading the most prominent group, the SA, Röhm participated in Hitler’s failed 1925 Munich Beer Hall Putsch aimed at seizing governmental power. Röhm was arrested but received a suspended prison sentence. Afterward Röhm became a Reichstag deputy, but broke with Hitler in 1925 over the future direction of the Nazi Party. Resigning from all positions Rõhm traveled to Bolivia to serve as an advisor to the Bolivian Army. However, at Hitler’s insistence, Röhm returned to Germany in 1930 and was officially appointed Chief of Staff of the SA in 1931. The organization then numbering over a million members, waa reorganized by Röhm. Its mission remained the same, engaging in campaigns of political violence against Communists, rival political parties, Jewish communities, and other groups. Despite praise from the party for his efforts with the SA, as public knowledge of his homosexuality gradually increased via the newsmedia, opposition to Röhm grew. Note that there was no issue with regard to homosexuality–essentially a crime in the Russian Federation–concerning Prigozhin. Yet, what has surfaced is an issue concerning him and narcotics abuse. Röhm maintained Hitler’s trust to the extent that once Hitler became Chancellor of Germany in 1933, he made Röhm Reichsleiter, the second highest political rank in the Nazi Party, and appointed him to the Reich Cabinet as a Reichsminister without portfolio. However, more problems arose from Röhm. In the years 1933 and 1934 when the Nazi government was consolidating it power, Röhm engaged in noisy rhetoric, calling for a “second revolution” that would transform german society that worried Hitler’s industrial allies. Further, Röhm continually demanded more power for the SA. The Reichswehr (German Armed Forces) saw the SA as a growing threat to its position. Hitler eventually saw his long-time friend as a threat to everything he was building and a potential political rival. Under Hitler’s orders, Reichfuhrer-SS Heinrich Himmler and the Deputy Reichfuhrer-SS and Director of Geheime Staatspolizei (Gestapo) Reinhard Heydrich purged the entire SA leadership during the infamous Night of the Long Knives on June 30,1934. Röhm was reportedly executed in a Munich prison on July 1, 1934
Prigozhin’s Mistakes
Putin broke his silence on Prigozhin’s jet crash on August 24, 2023 during a meeting with the head of the self-proclaimed Donetsk People’s Republic, Denis Pushilin, in the Kremlin. If readers can cast their minds back to Putin’s initial remarks, they may recall that Putin stated: “First of all, I want to express my sincere condolences to the families of all the victims, this is always a tragedy.” Putin went on to say: “I’ve known Prigozhin for a long time, since the early ’90′s.” He described him as “a talented man, a talented businessman.” Most relevant, Putin intriguingly added: “He was a man of difficult fate, and he made serious mistakes in life, and he achieved the results needed both for himself and when I asked him about it–for a common cause, as in these last months.” There were indeed many mistakes that Prigozhin made while ostensibly assisting Putin. Prigozhin had required but had not always warranted Putin’s forgiveness many times. Putin had forgiven much. To that extent, such is not so apparent as Putin mentioned that Prigozhin always did what he asked him to do. Often, Putin had to hold him at arms length. The list of disappointments is far lengthier than one might imagine as it concerned the failure to optimally serve Putin’s interests. It went far beyond Prigozhin’s ramblings about Ukraine. A small number are listed here.
Food Poisoning of Schoolchildren
As aforementioned, in 2007, under the National Education Project, the Russian Federation government sought to improve catering in educational institutions in fourteen of the country’s regions. They introduced a program titled “innovative on-board lunches” for Russian schoolchildren. In April 2008, a tender to provide “on-board meals” for 85 schools that had no cafeterias of their own was announced in St. Petersburg. Сonсord received the contract and began feeding St. Petersburg school children. To perform that task, Prigozhin opened a food processing plant outside St. Petersburg. Meduza reported that Putin attended the plant’s 2010 opening. In 2011, the parents of students began to protest the factory for providing their children with processed food packed with preservatives. According to Meduza, Prigozhin rather than succumb to the scandal, turned to Moscow, where he was awarded school catering contracts worth more than $177 million. Through companies affiliated with Concord, Prigozhin eventually began supplying food to schools beyond Moscow, to include: Krasnodar, Kaliningrad, Pyatigorsk, the Khabarovsk region, Yekaterinburg, the Zabaykalsky region, and the Yaroslavl region. There were further cases of poisoning and complaints about the food. In ten years, over 1,000 lawsuits for the total amount of $43 million were filed against his affiliate companies.
Fumbled Effort To Interfere with the 2016 US Elections.
By 2016, Prigozhin signed several federal government contracts totaling at least $3.1 billion. Prigozhin is linked to the oil industry as well. His companies reportedly received a percentage of Syria’s oil revenue in exchange for protecting its oil fields from the virulent Islamic terrorist organization, ISIS. As noted earlier, a portion of the profits from his contracts with the Russian Federation Defense Ministry are alleged to have been used to start and fund the Internet Research Agency. The Internet Resource Agency, known also as Glavset, is a St. Petersburg-based technological company seeking to promote disinformation campaigns both domestically and abroad. In its initial operations, Glavset sought to put down domestic protests by creating counterfeit social media accounts that advocated on behalf of Putin and disparaged the actions of his primary opponent, Aleksei Navalny. However, its operations expanded to the point of interfering with elections internationally, including those within the US in 2016. Alleged evidence of Prigozhin’s involvement in the US election meddling is his meeting with Mikhail Bystrov, the appointed head of Glavset, several times between 2015 and 2016 to discuss work being performed. Considered notable among those certain of Prigozhin’s role in the matter is the fact that Glavset’s “Project Lakhta”, known to be a disinformation campaign, received approximately $1.2 million in funding from Bystrov in 2016 alone. A grand jury in the US federal court system, used the term “troll farm” to describe the Internet Research Agency and determined that it was used to meddle in the 2016 US Presidential Elections. A reward of up to $250,000 has been offered by the US Federal Bureau of Investigation for information leading to the arrest of Prigozhin.
In November 2017, Putin surely went to Hanoi G20 Summit within interest in discussing with the new US President, Donald Trump, a variety of issues to include, very important to him, the Russia and Moldova Jackson-Vanik Repeal and Sergei Magnitsky Rule of Law Accountability Act of 2012 (The Magnitsky Law), which had a devastating impact on the ability of oligarchs and other business leaders to operate in the US and alongside US businesses. Yet, as a consequence of the foul-up of Prigozhin’s organization in its effort to impact national elections in the US in 2016, Trump reportedly bombarded Putin with questions about the Russian Federation’s interference in Hanoi. It was to a degree, an embarrassment for Putin. As with other Western newsmedia sources, on November 11, 2017, in Agence France-Presse, it was headlined that Putin and Trump talk Syria, election meddling at their brief meeting. No mention was made of the Magnitsky issue
US President Donald Trump (right) speaks with Putin (left) during a stroll in Hanoi Vietnam on November 11, 2017. By 2016, Prigozhin signed several federal government contracts totaling at least $3.1 billion. A portion of the profits from his contracts with the Russian Federation Defense Ministry were alleged to have been used to start and fund the Internet Research Agency. The Internet Resource Agency, known also as Glavset, was a St. Petersburg-based technological company seeking to promote disinformation campaigns both domestically and abroad. In its initial operations, Glavset sought to put down domestic protests by creating counterfeit social media accounts that advocated on behalf of Putin and disparaged the actions of his primary opponent, Aleksei Navalny. However, its operations expanded to the point of interfering with elections internationally, including those within the US in 2016. A grand jury in the US federal court system, used the term “troll farm” to describe the Internet Research Agency and determined that it was used to meddle in the 2016 US Presidential Elections. A reward of up to $250,000 was offered by the US Federal Bureau of Investigation for information leading to the arrest of Prigozhin. In November 2017, Putin surely went to Hanoi G20 Summit with an interest in discussing with the new US President, Donald Trump, a variety of issues to include, very important to him, the Russia and Moldova Jackson-Vanik Repeal and Sergei Magnitsky Rule of Law Accountability Act of 2012 (The Magnitsky Law), which had a devastating impact on the ability of oligarchs and other business leaders to operate in the US and alongside US businesses. Yet, as a consequence of the foul-up of Prigozhin’s organization in its effort to impact national elections in the US in 2016, Trump reportedly bombarded Putin with questions about the Russian Federation’s interference in Hanoi. It was to a great degree, an embarrassment for Putin.
Wagner Group Attrocities in Bucha, Ukraine
The Kremlin could barely suggest that it had acted in the interest of international peace and security when it invaded Ukraine or took previously in just about any other intervention externally during Putin’s era of leadership. Nonetheless, it made every effort to sell its case, pressing its narrative on Ukraine. The last thing the Kremlin wanted to contend with were reported large scale atrocities, with evidence alleged caught by Western newsmedia cameras. That was the circumstance Prigozhin created, after the Wagner Group left the town of Bucha.
Via the Agence France-Presse on April 7, 2022, the Times of Israel published a report that German intelligence services intercepted radio traffic of Russian soldiers discussing the killings of civilians in Bucha. The Agence France-Presse used the renowned German newmedia source, Der Spiegel, which cited a closed-door briefing given by Germany’s foreign intelligence service BND. In the Bundestag. Der Spiegel reported that the audio files ofthe BND gleaned at the Bundestag briefing provided evidence of the Wagner mercenary group’s role in the atrocities. Der Spiegel said the audio files intercepted by the BND also provide evidence of the Wagner mercenary group’s role in the atrocities. The German government said its satellite images from last month from the period of March 10, 2022 to March 18, 2022, and reliable evidence showed that Russian Federation forces and security units were deployed in this area from March 7, 2022 until March 30, 2022. The Kremlin denied the accusations of mass killings. It claimed that the images emerging from Bucha were “fakes” or that the deaths occurred after Russian Federation troops withdrew from the town.
In the West, Putin’s regime is looked upon as one in which the powers of evil are exalted. Under the leadership of Prigozhin, the Wagner Group in Bucha helped to hammer in that idea with the West and much of the world. Prigozhin did not help the Kremlin’s situation.
Prigozhin’s Refusal To Have the Wagner Group Sign an Oath of Allegiance and Contracts with the Russian Federation Defense Ministry
Before the Wagner Group Rebellion transpired, seemingly many of the organization’s troops sensed big trouble ahead. That sense stemmed from controversy stirred over an order from the Federation Defense Minister on June 10, 2023 requiring all “volunteer detachments” to sign contracts with his ministry by the end of that month. The Russian Federation Defense Ministry explained that order was given by Shoigu in the interests of increasing the effectiveness of “volunteer detachments”, all such units–or their men–would have to sign a contract with the Russian Federation Defense Ministry by July 1, 2023. The order did not mention the Wagner Group by name. However, it was understood then that it routinely referred to the organization as “volunteer assault detachments”. As for the rationale behind the order, the Russian Federation Defense Ministry claimed: “This will give the volunteer formations the necessary legal status, create unified approaches to the organisation of comprehensive provision and fulfilment of their tasks. Russian Federation Deputy Defense Minister Nikolai Pankov shared: “These measures will increase the combat capabilities and effectiveness of the armed forces and their volunteer detachments.”
The following day, Prigozhin publicly stated that his Wagner Group troops would not sign any contract with Shoigu. Prigozhin viewed the order as an attempt by Shoigu to take control of the Wagner Group. Prigozhin suggested that the Defense Ministry might use the failure to comply with the order as a reason to deprive Wagner of supplies. Prigozhin stated: “What could happen after this order is that they will not give us weapons and ammunition. We will figure it out, as they say.” He went on to say: “But when the thunder breaks, they will come running and bring weapons and ammunition with a request to help.” The entire episode created a further rift between Shoigu and Prigozhin. It surely caused Putin additional distress. Most of the Wagner Group troops did not sign the Defense Ministry contracts then. However, some in a bid to distance themselves from the dangerous controversy, left the Wagner Group, moving away from the situation, and signed the contracts in order to ply their trade with other private military companies and the Defense Ministry, too. Chacun voit midi à sa porte.
Prigozhin’s Bizarre Video Recordings from Rostov-on-Don during the Wagner Group Rebellion
The Wagner Group Rebellion may very well have beenmay very well have been some preconceived plan of action developed by Putin and his advisers for domestic political purposes. It would not be too hard to imagine that in Putin’s Russia, a decision may have been made to stage a crisis with the objective of drawing attention away from actual events on the battlefield in Ukraine using a staged rebellion in the concerning events in Ukraine. Among its ingredients, there was the agent provocateur, the very agitated, highly-aggressive owner of the Wagner Group, Prigozhin. The threat was a very capable military force moving on Moscow of all places. The cause and target of the insurrection was not Putin, whose authority is beyond question–woe to those who would suggest it even as part of an all important artifice. The cause and targets of the uprising were Shoigu and Gerasimov, who anyone and everyone in the Russian Federation had recognized, even if just quietly with, as having dreadfully failed to conduct the special military operation in Ukraine in an effective way. Yet, even if Prigozhin and his rebellious Wagner Group troops mirrored feelings broadly felt by the Russian people and put them on the front burner, the Russian people would also expect Putin to be Putin: to flex his muscles; to demonstrate his power and control; to assert his authority; to defend the country from a threat; to establish law and order; and, to bring the wrong-doers to justice. He had the perfect and ample opportunity to do it all. Putin and advisers knew the Russian people would admire him for it. Marcet sine adversario virtus. (Valor becomes feeble without an opponent.)
Important attendant domestic political benefits of the artifice suggested would be a significant increase in Putin’s popularity among the Russian people generally; the ratcheting up of a sense among the Russian people that Putin is in complete control of the country and his authority is not subject to challenges; a reinvigoration of the Russian spirit to prevent any chance of the country sleepwalking psychically to decline; and, very importantly stemming any sense of the regime’s decline. Yet of the utmost importance, in the midst of all that was going wrong in Ukraine, on the grand stage before the Russian people and the world, Putin scored a victory. He was the champion over the rebels. That victory would be savored by Putin and his advisers and expectedly, the Russian people. Recall from his Wagner Group Rebellion addresses that he magnanimously shared credit for the accomplishment with members of the government and the Russian people.
Still, there were also unnecessary ad-libs Prigozhin made on video recordings from Rostov-on-Don broadcast and posted online during the Wagner Group Rebellion. Some were dangerously threatening and perceivably seditious. As the matter continued,which naturally appeared grave, Prigozhin’s continued comments dipped into the realm of the absolute absurd. Well over the top were his remarks on video on the morning of June 24, 2023 from Roostov-on-Don in which he rashly stated: “Everyone who will try to put up resistance . . . we will consider it a threat and destroy it immediately, including any checkpoints that will be in our way and any aircraft that we see over our heads. I am asking everyone to remain calm and not succumb to provocations, stay in their homes. It is advisable not to go outside along the route of our movement.” He went further off the mark when he bizarrely declared: “Once again I’m warning everyone: we will … destroy everything around us. You can’t destroy us. We have goals. We are all ready to die. All 25,000 of us.”
Prigozhin was putting his unique “golden touch” on the whole matter likely creating some concern and considerable stress among many in the Kremlin as to whether everything would come together as planned. that stress was doubtlessly felt by Putin at the time. If Prigozhin and the Wagner Group would have had hypothetically driven into Moscow and would have taken control of the Russian Federation Defense Ministry, the outcome for them would not have reminded anyone who would have observed their march much as the renowned final stands of glory such the The Alamo (1836 )in what was then the Texas Territory or the Battle of Camerone (1863) in Mexico. It most likely would have closely resembled something akin to Colonel Armstrong Custer’s Last Stand at the Battle of Little Big Horn (1876), a complete massacre with no appreciable positive ououtcome. With his words, he had what his troops could not have, a damaging psychological impact on the psyche of the Russian people. He made the government appear vulnerable.
The Appearance of Complicity with Russian Federation General Sergei Surovikin.
A real tragedy that cropped from Prigozhin’s position as owner of the Wagner Group was his seemingly unfettered engagement with the general staff and other senior generals of the Russian Federation Armed Forces due to his close association with Putin more so than his ownership of the organization. Such a political association in the Russian Federation and just about any country is very tricky business for a senior military commander. It must be handled tactfully and delicately. If not, a fine career can easily be shipwrecked. One association which Prigozhin spoke of often was that with the Commander-in-Chief of Vozdushno-kosmicheskiye sily (the Russian Aerospace Forces) or VKS General of the Army Sergei Surovikin. During the invasion of Ukraine, Surovikin who was once commander of the Joint Group of Forces in the Special Military Operation zone later became Deputy commander in the Southern “Grouping” of the Special Military Operation zone where the Wagner Group operated and has bases. Surovikin had also worked with the Wagner Group while serving two tour in Syria in 2017. Surovikin began his first of two tours in Syria. On June 9, 2017, Surovikin was introduced to the newsmedia as the Commander of the Russian Federation Armed Forces deployed to Syria. Among Russians who welcomed the appointment of Surovikin when he took command in Ukraine was Prigozhin. In a statement put out at the time by Concord, Prigozhin said: “Surovikin is the most able commander in the Russian Army.” He called Surovikin a “legendary figure, he was born to serve his motherland faithfully.” He noted: “Having received an order [in 1991], Surovikin was that officer who without hesitation got in his tank and went forward to save his country.”
However, beyond being a friend of Putin and owner of Wagner Group which often operated with the Russian Federation Armed Forces, there were no personal reasons and perhaps no reasons for to be a close associate of Surovikin or any general. Prigozhin was not a professional soldier. He owned the Wagner Group just short of 10 years and training as it’s commander was on the job and surely limited. Unlike Surovikin, Prigozhin did not graduate from the Omsk Higher Military School. He did not begin his career serving as a lieutenant in the Voyská Spetsiálnogo Naznachéniya (Special Purpose Military Units) or spetsnaz. He did not graduate from the renowned Frunze Military Academy.. He did not graduate from Voyennaya Akademiya General’nogo Shtaba Vooruzhennykh Sil Rossijskoj Federacii (the Military Academy of the General Staff of the Russian Federation). Discussions with him on military matters must be somewhat trying at times. Surovikin certainly was not a billionaire oligarch much as Prigozhin. From what was known publicly, he had no obvious prospect of ever becoming one. Prigohzin could not make him one. The relationship between Prigozhin and Surovikin was likely superficial for the most part. Yet, because it was enough that the two were talking at all was enough to cause sufficient suspicion on Surovikin with regard to Prigozhin’s thinking during the Wagner Group Rebellion. To that extent, Surovikin was to suffer as a result of guilt by association. Indeed, ostensibly in great part due to a number of well-publicized links between Surovikin and Prigozhin that fuelled rumors of the general’s alleged strong ties with the Wagner Group, there was apparently more than enough for security service investigators to sink their teeth into. There was also the fact the Wagner Group Rebellion was unluckily launched from Surovikin’s Southern sector in Ukraine into the Russian Federation. Surovikin was detained by the security services on June 23, 2023. It was the starting date of the Wagner Group Rebellion. Reports of Surovikin’s release from detention surfaced in the newsmedia in the West on September 4, 2023. It was reported at the same time that his service in the Russian Federation Armed Forces was terminated.
Prigozhin created an “unsafe” environment for Surovikin, politically. Perhaps Putin had a good idea of how and why the general had gotten entangled with Prigozhin and the Wagner Group Rebellion. However, he did not stop what transpired, at least not right away. Putin did not take any chances. The regime still worked against the general–particularly with endless “interviews”–in the way that is does. Being heavy-handed as they typically, no thought was likely given the dynamics of the relationship between Prigozhin, a friend of Putin, and Surovikin. No consideration given to that fact that Surovikin was already swamped by the need to handle an on-coming counteroffensive of Zbrojni syly Ukrayiny (the Ukrainian Armed Forces) and could not dedicate any real time Prigozhin’s puzzle. No concern was likely given to the significant gap between Surovikin’s military knowledge, experience and education, with Prigozhin, who relatively was lacking on the subject. There could not have been any great discussion between the two on dealing with Shoigu–who also never receive formal military training and education–and Gerasimov or the Russian Federation’s struggle in Ukraine in general. Based on information from various sources, the newspaper of record in the US, the New York Times, reported on September 4, 2023, the security services seemed to open their eyes wide enough to notice there was reason, not even a good imaginary one, for Surovikin to remain in detention. The Russian Federation security services released him.
Prigozhin looks over maps of the tactical situation in Bakhmut, Ukraine in 2023 (above). A real tragedy that cropped from Prigozhin’s position as owner of the Wagner Group was his seemingly unfettered engagement with the general staff and other senior generals of the Russian Federation Armed Forces due to his close association with Putin more so than his ownership of the organization. Such a political association was very tricky business for a senior military commander in a regime such as Putin’s, and had to handled tactfully and delicately. Beyond being a friend of Putin and owner of Wagner Group which often operated with the Russian Federation Armed Forces, there were no personal reasons and perhaps no reasons for to be a close associate of any general. Prigozhin was not a professional soldier. He had owned the Wagner Group for just short of 10 years and his training as its commander was “on the job” and surely limited. Unlike Surovikin, Prigozhin did not graduate from the Omsk Higher Military School. He did not begin his career serving in the Voyská Spetsiálnogo Naznachéniya (Special Purpose Military Units) or spetsnaz. He did not graduate from the renowned Frunze Military Academy. He did not graduate from Voyennaya Akademiya General’nogo Shtaba Vooruzhennykh Sil Rossijskoj Federacii (the Military Academy of the General Staff of the Russian Federation). Discussions with him on military matters must be somewhat trying for senior military officers at times.
Embezzlement at Concord or the Wagner Group Specifically?
There may very well have been issues aggravating Putin concerning the skimming of profits from government payment to the Wagner Group for its contract services. Putin oddly hinted at this possibility in a speech, but did not offer much evidence on the villainy. For him to even broach to matter publicly was a powerful act in itself. On June 27, 2023, Putin’s fourth of four major addresses on the Wagner Group Rebellion, initially he spoke to personnel of the Russian Federation Defense Ministry,.However, as explained in greatcharlie’s August 1, 2023 post entitled, “The Wagner Group Rebellion: Insurrection or Staged Crisis? A Look Beyond the Common Wisdom (Part 2)”, what began as a simple speech on the role of the Russian Federation Armed Forces in halting the Wagner Group Rebellion and some general military matters to military personnel oddly became an effort by Putin to lay out some facts about the Wagner Group that in the context of the event might have appeared disturbing to discerning ears. Putin explained how the Russian Federation government was always the resource–the engine–that funded, supplied, and energized the Wagner Group. In his own words, Putin stated: “I would like to point out, and I want everyone to be aware of the fact that all of the funding the Wagner Group received came from the state. It got all its funding from us, from the Defence Ministry, from the state budget. Between May 2022 and May 2023 alone, the Wagner Group received 86,262 million rubles from the state to pay military salaries and bonuses, including 70,384 million rubles for payroll and 15,877 million rubles for paying out bonuses. Insurance premiums totalled 110,179 million.” Putin admitted plainly that all of the activities of the Wagner Group were funded by the Russian Federation government. To that extent, via Prigozhin and his firm Concord, the Wagner Group Rebellion was completely funded by the Russian Federation government. In its operations, the Wagner Group was under contract and under obligation to obey the orders of the Russian Federation government, no matter how recherché those orders might be. Without funding from the steady stream of funding from the Russian Federation government, the Wagner Group could not hope to go a jot farther.
Casting aspersions on Prigozhin came next. About “his Wagner Group”, Putin stated: “But while the state covered all of the Wagner Group’s funding needs, the company’s owner, Concord, received from the state, or should I say earned, 80 billion rubles through Voentorg as the army’s food and canteen provider. The state covered all its funding needs, while part of the group–I mean Concord–made 80 billion rubles, all at the same time. I do hope that no one stole anything in the process or, at least, did not steal a lot. It goes without saying that we will look into all of this.” Of course, no one would know these figures better than Putin. He was the one who ultimately decided to compensate Prigozhin–pay Concord–with those massive amounts. If the allegations of Embezzlement were true, the implications were tremendous. There would ne punishment. Prigozhin was not named directly by Putin in his fourth address. Looking at the speech today, there was no pretension. Nothing good was in the making by that time.
Prigozhin’s Final Mistake?
It remains possible that there was some new mistake, some new transgression, unknown to the public, over which Putin reached his peak. Conceivably, in the not so distant future, that hypothesized mistake might be made known by Putin, himself. In all honesty, greatcharlie believes that is somewhat unlikely for as it was suggested earlier, Putin surely wants the matter of Prigozhin to remain closed forever. He will unlikely be the one to dredge it up again. Perhaps such any imaginable that independent newsmedia houses may hear whisper about some new and final mistake by Prigozhin. Such whisper might very well become a popular topic of among journalists and well-known Kremlin watchers in the Russian Federation. It might also become known those in the opposition movement, the fount of all juicy rumor and gossip about Putin. Yet, then again, it may be the case that they, too, have had their fill on the Prigozhin matter. Prigozhin and his men were engaged in a dark, dangerous business, in which the deaths of others and monetary gain were the only “rewards.” He and his commanders met their fate while engaged in that work, and perhaps only a precious few in the independent newsmedia as well as in opposition political circles in Russian Federation might be moved enough to shed tears for them.
More likely, however, the last on the possible list of mistakes are actions by Prigozhin that could only have left Putin better than annoyed with him. Indeed, in the abstract, greatcharlie can only presume Putin was particularly displeased with Prigozhin’s continued counter messaging on Ukraine well after the Wagner Group Rebellion. He suggested Africa was where the Wagner Group should direct its talents. He declared that Africa should be the Wagner Group’s priority. Prigozhin publicly stated that he wanted to recruit Bogatyrs-rough men–for Africa. He expressed no desire to have his organization serve in Ukraine. He made it clear that Ukraine was a non-issue for the Wagner Group. It is possible that he believed in speaking this way, he was very apparently lashing out at Shoigu and Gerasimov and not Putin’s government or Putin, himself. Yet, at this point, Putin unlikely wanted to hear too much more about the Wagner Group and what it could not do for him. After all, the Wagner Group Rebellion was settled.
When meeting with Prigozhin after the Wagner Group Rebellion,, Putin most likely made it clear to Prigozhin that he want he wanted no more negative, noisy talk on Ukraine. it would have been delinquent for him to do otherwise. One might imagine that Putin warned that there would be no second chance as too much was at stake. There was indeed a line that could not be crossed and it might be said by observers, inside and outside the Russian Federation, that Prigozhin had already crossed it more than once. Putin’s likely issuance of a warning to Prigozhin takes greatcharlie’s thought to the fateful discussion between the Great Shawnee Tribe Chief, Tecumseh and the Governor Willian Tyler in 1811 concerning White settlers further westward expansion into Native controlled land. Beginning in 1808, the Shawnee leader Tecumseh travelled throughout the US gathering supporters and allies to form a native confederacy that could resist westward expansion by white settlers. In August 1811, Tecumseh met with Governor William Henry Harrison to discuss the recent treaties, land purchases, and violence throughout the Indiana territories. At their meeting, Tecumseh spoke for a large group of natives along the Great Lakes, and told Harrison, “that piece of land, we do not wish you to take it,” indicating that his allies wanted “the present boundary line to continue.” Should the whites continue their expansion into the region, Tecumseh warned, “I assure you it will be productive of bad consequences.”
Putin is no longer a young president filled with thoughts and excitement about a bold future ahead. He has accomplished much. There were close associates, friends, who came with him for the ride onward and upward, to include Prigozhin. Most were kept close even with all of their mistakes. Perhaps the cause for that in part has been Putin’s sense of humor. In the case of Prigozhin, however, there was every indication that any further association with him had to end. His behavior could have potentially marred all that the Russian Federation President created and was creating. Putin may have logically concluded that all he had achieved and surely wanted to complete before his end was being put in some jeopardy by Prigozhin. Far more was at stake than friendship and nostalgia. At stake for Putin and others operating at the highest levels of government were the Russian Federation’s interests and aims, its survival. There was every indication that any continued association with Prigozhin or any attempt to further countenance of his behavior might potentially have been further disruptive, if not destructive.
To be sure, the impact of Prigozhin’s final verbal blows, albeit unintended to harm Putin, were certainly felt by the Russian Federation President. Surely behind the Kremlin’s walls, it was likely apparent that Prigozhin was out of control. Perhaps all elites with real influence in Moscow could see that and were flummoxed by events since February 24, 2022, the starting date of the special military operation.
It seems that by the time Prigozhin was going off on further tangents following the Wagner Group Rebellion, telling his troops to focus on Africa and the need for the organization to recruit bogatyrs for Africa, he had likely passed everyones point of no return except Putin. Putin being Putin, however,, was not going to be forever disposed to hang on a knife’s edge over what fantastic outrage Prigozhin would utter or engage in next. Putin needed the Russian people to support the special military operation, the invasion of Ukraine. Casting doubt about the special military operation for any selfish reason, for any reason, particularly after the Wagner Group Rebellion was over, was unacceptable to him. Putin was not going to wait to find out if new, greater damage was being done by Prigozhin’s declarations on Ukraine and disparagement of the war effort.
Annum iam tertium et vicesimum regnat. (He has been reigning for twenty-three years.) To gnaw a bit further on the matter, Putin, is no longer a young president filled with the thoughts and excitement about the future ahead. He has accomplished much. There were close associates, friends, who came with him for the ride onward and upward, to include Prigozhin. Most were kept close even with all of their mistakes. Perhaps the cause for that in part has been Putin’s sense of humor. In the case of Prigozhin, however, there was every indication that any further association with him had to end. His behavior could have potentially marred all that the Russian Federation President created and was creating. Putin may have logically concluded that all he had achieved and surely wanted to complete before his end was being put in some jeopardy by Prigozhin. Far more was at stake than friendship and nostalgia. At stake for Putin and others operating at the highest levels of government were the Russian Federation’s interests and aims, its survival. There was every indication that any continued association with Prigozhin or any attempt to further countenance of his behavior might potentially have been further disruptive, if not destructive. Order must be maintained in the Russian Federation. Prigozhin managed to become a strain that he could no longer tolerate. He could not allow the special military operation to flounder as result of Prigozhin’s problems with Shoigu and Gerasimov and simply his continued stupidities. There was nothing even slightly humorous about any of it.
Putin could no longer hope to save his friend. He could only go one direction on the matter. That did not necessarily mean Prigozhin had to be killed. Perhaps it would be enough to state fate stepped in.
Discussion will be extended in Part 2, to be published later.